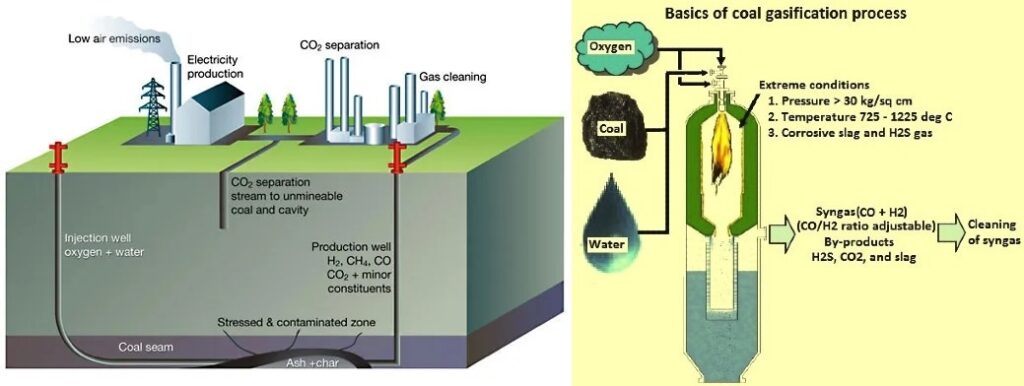
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy production, the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable technologies has become a paramount objective for nations worldwide. Russia, a global energy powerhouse, is witnessing a notable shift in its corporate sector as companies increasingly embrace gasification as a key strategy for cleaner energy production. This blog will delve into the compelling reasons behind the surge in gasification adoption among companies in Russia, exploring the environmental benefits, economic considerations, and the transformative impact this technology is having on the nation’s energy landscape.
The Evolution of Russia’s Energy Sector:
Legacy Challenges:
1.1 Dependency on Conventional Energy Sources:
Historically, Russia has heavily relied on conventional energy sources, particularly fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. While these resources have fueled economic growth, they come with significant environmental implications, including greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
1.2 Environmental Pressures:
Growing global awareness of climate change and environmental degradation has put pressure on nations, including Russia, to reassess their energy strategies. The need for sustainable alternatives has prompted a reevaluation of energy production methods to align with international environmental commitments.
Gasification as a Sustainable Energy Solution:
Understanding Gasification:
2.1 Cleaner Energy from Waste:
Gasification stands out as a promising technology that converts various carbon-containing materials, including waste, into clean and versatile synthesis gas (syngas). This syngas can be used for power generation, reducing the reliance on traditional fossil fuels and offering a cleaner alternative to conventional energy sources.
2.2 Diverse Feedstock Utilization:
One of the key attractions of gasification is its ability to process diverse feedstocks. Whether it’s municipal solid waste, agricultural residues, or industrial by-products, gasification provides a flexible solution for companies looking to reduce their environmental footprint by efficiently managing different types of waste.
Environmental Benefits Driving Adoption:
Emission Reduction and Air Quality Improvement:
3.1 Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Gasification operates as a nearly carbon-neutral process, mitigating the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production. Companies adopting gasification can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
3.2 Particulate Matter Reduction:
Unlike traditional combustion methods, gasification produces syngas with lower particulate matter emissions. This translates to improved air quality, reducing health risks for both the workforce and surrounding communities. The emphasis on cleaner air has become a driving force behind the adoption of gasification technologies.
Economic Considerations and Energy Security:
Diversification of Energy Sources:
4.1 Reducing Dependency on Imports:
Russia’s strategic move to adopt gasification aligns with its goal to reduce dependency on energy imports. By diversifying energy sources and utilizing domestic waste as a feedstock, companies contribute to enhanced energy security, ensuring a more resilient and self-sufficient energy infrastructure.
4.2 Stable Energy Prices:
Gasification offers the advantage of stable and potentially lower energy prices over the long term. Companies investing in gasification technologies can achieve cost predictability, shielding themselves from the volatility often associated with global energy markets.
4.3 Economic Growth and Job Creation:
The deployment of gasification projects stimulates economic growth by creating jobs and fostering innovation. The establishment of gasification facilities, coupled with the development of associated industries such as syngas utilization and biofuel production, contributes to job creation and economic development in the regions where these projects are implemented.
Technology Advancements and Innovation:
Efficiency Improvements:
5.1 Advanced Gasification Technologies:
Ongoing research and development efforts in Russia are focused on advancing gasification technologies to enhance efficiency. Innovative gasification reactors, improved temperature and pressure control, and optimized syngas cleaning processes contribute to more efficient and reliable energy production.
5.2 Integration with Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems:
Gasification systems are increasingly integrated with Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems, maximizing the utilization of generated heat. This integration not only enhances the overall efficiency of the gasification process but also improves the economic viability of waste-to-energy projects.
Strategic Government Support:
Government Initiatives and Incentives:
6.1 Policy Support for Cleaner Energy:
The Russian government has recognized the significance of cleaner energy production and has implemented policies to support the adoption of gasification technologies. Incentives, subsidies, and favorable regulatory frameworks encourage companies to invest in sustainable energy solutions, fostering a conducive environment for gasification projects.
6.2 Strategic Environmental Goals:
Aligning with international environmental commitments, Russia has set ambitious goals to reduce its carbon footprint. Gasification aligns with these strategic objectives, making it a preferred choice for companies seeking to contribute to the nation’s broader sustainability agenda.
Case Studies: Pioneering Gasification Projects in Russia
Success Stories:
7.1 The Syktyvkar Biogas Plant:
The Syktyvkar Biogas Plant stands as a testament to the success of gasification in Russia. This facility utilizes gasification technology to convert organic waste into biogas, showcasing the potential for gasification to contribute to renewable energy production and waste management.
7.2 Corporate Initiatives:
Several leading companies in Russia have embraced gasification as part of their corporate sustainability initiatives. These companies are not only meeting their energy needs but also playing a pivotal role in shaping the narrative of cleaner energy production in the country.
Future Outlook and Global Collaboration:
Advancements in Gasification Technologies:
8.1 Next-Generation Gasification:
Ongoing research in Russia is directed towards developing next-generation gasification technologies. These advancements aim to enhance the scalability, efficiency, and versatility of gasification processes, opening up new possibilities for waste management and resource recovery.
8.2 Global Collaborations:
Russia actively engages in international collaborations to exchange knowledge and best practices related to gasification. Collaborative projects with countries at the forefront of sustainable energy technologies contribute to a global effort to address environmental challenges.
Conclusion:
The surge in gasification companies in Russia marks a transformative shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy production. Driven by environmental consciousness, economic considerations, and technological advancements, gasification has become a linchpin in Russia’s journey towards a more resilient and eco-friendly energy landscape. As more companies join this paradigm shift, the nation is poised to emerge as a leader in the global transition towards cleaner and greener energy solutions. Gasification is not just a technological innovation; it represents a strategic investment in a future where sustainability and economic prosperity go hand in hand.